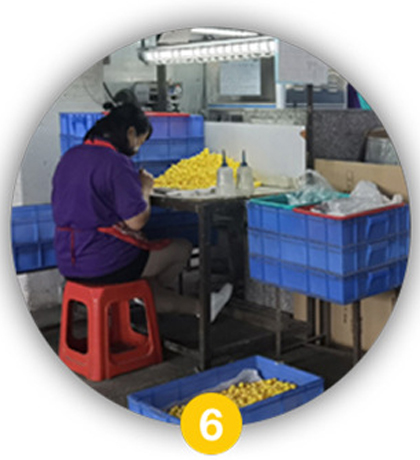
QC Check
A rigorous Quality Control inspection is performed on the newly moulded plastic parts. Inspectors check for defects such as flash (excess plastic), sink marks, short shots (incomplete filling), warping, and colour consistency to ensure they meet the required standards before advancing to decoration.
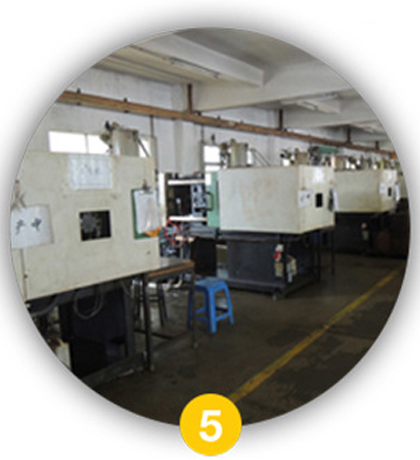
Production
The mass manufacturing process begins using the finished mould. Plastic pellets are melted and injected under high pressure into the mould cavity in an Injection Moulding machine. The plastic cools and solidifies, forming the toy’s components, which are then ejected. This cycle repeats to produce the required quantity.
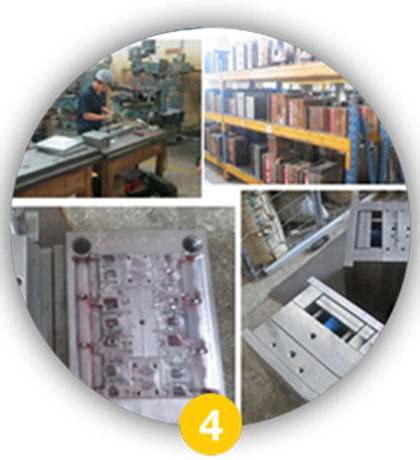
Mould
A precision tool, typically made from hardened steel or aluminum, is crafted. This mould is a negative impression of the toy’s parts, created using CNC machining and electrical discharge machining (EDM). Its quality is critical, as it will define the surface finish and dimensional accuracy of every toy unit produced.
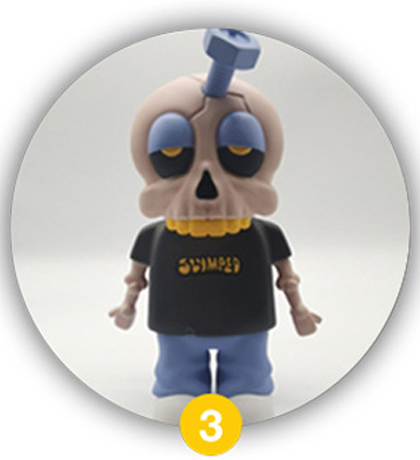
Hand-Painted Mock-up
Based on the approved white mock-up, a craftsman meticulously paints a sample by hand to visualize the final color scheme, details, and aesthetic. This model acts as the master color guide, establishing the painting standards and techniques required for the mass-production phase.
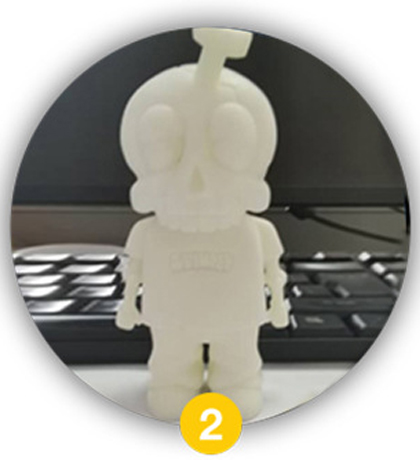
White Mock-up
A physical prototype is produced from the 3D file, typically using a 3D printer (SLA or SLS) or CNC machining. This model, often made from a white resin or plastic, is unpainted. Its purpose is to verify the toy’s physical form, proportions, structural integrity, and fit of moving parts before investing in the mould.
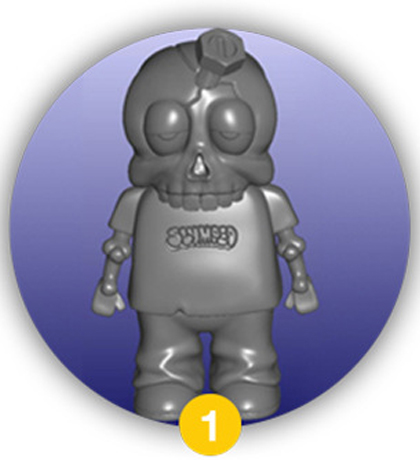
3D File
A digital 3D model of the toy is created or finalized using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This file serves as the digital blueprint for the entire project, defining all dimensions, geometries, and structural details. It is used for prototyping, and later, to program the machines that will create the mould.